多线程并发推理¶
单线程的推理服务,往往由于无法实现较高QPS,而导致GPU利用率过低。利用多线程实现并发推理,能提高推理服务的吞吐量,实现推理服务的优化。
利用多线程来实现并发推理¶
使用示例¶
下面的示例以C++为例。
多线程实现¶
1、创建Predictor
auto main_predictor = paddle_infer::CreatePredictor(config);
2、创建多个推理线程并执行
std::vector<decltype(main_predictor)> predictors;
for (int i = 0; i < FLAGS_thread_num - 1; ++i) {
predictors.emplace_back(std::move(main_predictor->Clone()));
}
predictors.emplace_back(std::move(main_predictor));
std::vector<std::thread> threads;
auto begin = time();
for (int i = 0; i < FLAGS_thread_num; ++i) {
threads.emplace_back(Run, predictors[i], i);
}
Run() 为线程执行函数,以下代码片段供参考。
void Run(std::shared_ptr<Predictor> predictor, int thread_id) {
auto run_one_loop = [&](int batch_size) {
// input
int channels = 3;
int height = 224;
int width = 224;
int input_num = channels * height * width * batch_size;
std::vector<float> in_data(input_num, 0);
for (int i = 0; i < input_num; ++i) {
in_data[i] = i % 255 * 0.1;
}
auto in_names = predictor->GetInputNames();
auto in_handle = predictor->GetInputHandle(in_names[0]);
in_handle->Reshape({batch_size, channels, height, width});
in_handle->CopyFromCpu(in_data.data());
CHECK(predictor->Run());
// output
auto out_names = predictor->GetOutputNames();
auto out_handle = predictor->GetOutputHandle(out_names[0]);
std::vector<float> out_data;
std::vector<int> out_shape = out_handle->shape();
int output_num = std::accumulate(out_shape.begin(), out_shape.end(), 1,
std::multiplies<int>());
out_data.resize(output_num);
out_handle->CopyToCpu(out_data.data());
float mean_val = std::accumulate(out_data.begin(), out_data.end(),
decltype(out_data)::value_type(0));
// std::cout << "mean: " << mean_val << std::endl;
};
for (int i = 0; i < FLAGS_loop_times; ++i) {
run_one_loop(FLAGS_batch_size);
}
}
使用PredictorPool的多线程实现¶
Paddle Inference提供了Predictor线程池的封装。
1、创建Predictor Pool
paddle_infer::services::PredictorPool pred_pool(config, thread_num);
2、创建多个推理线程并执行
std::vector<std::thread> threads; auto begin = time(); for (int i = 0; i < FLAGS_thread_num; ++i) { threads.emplace_back(Run, pred_pool.Retrive(i), i); }
Run() 为线程执行函数,同上。
多线程并发推理测试¶
测试环境
NVIDIA® T4 GPU
CUDA 11.2.2
cuDNN 8.2.1
PaddlePaddle 版本:v2.3
测试结果
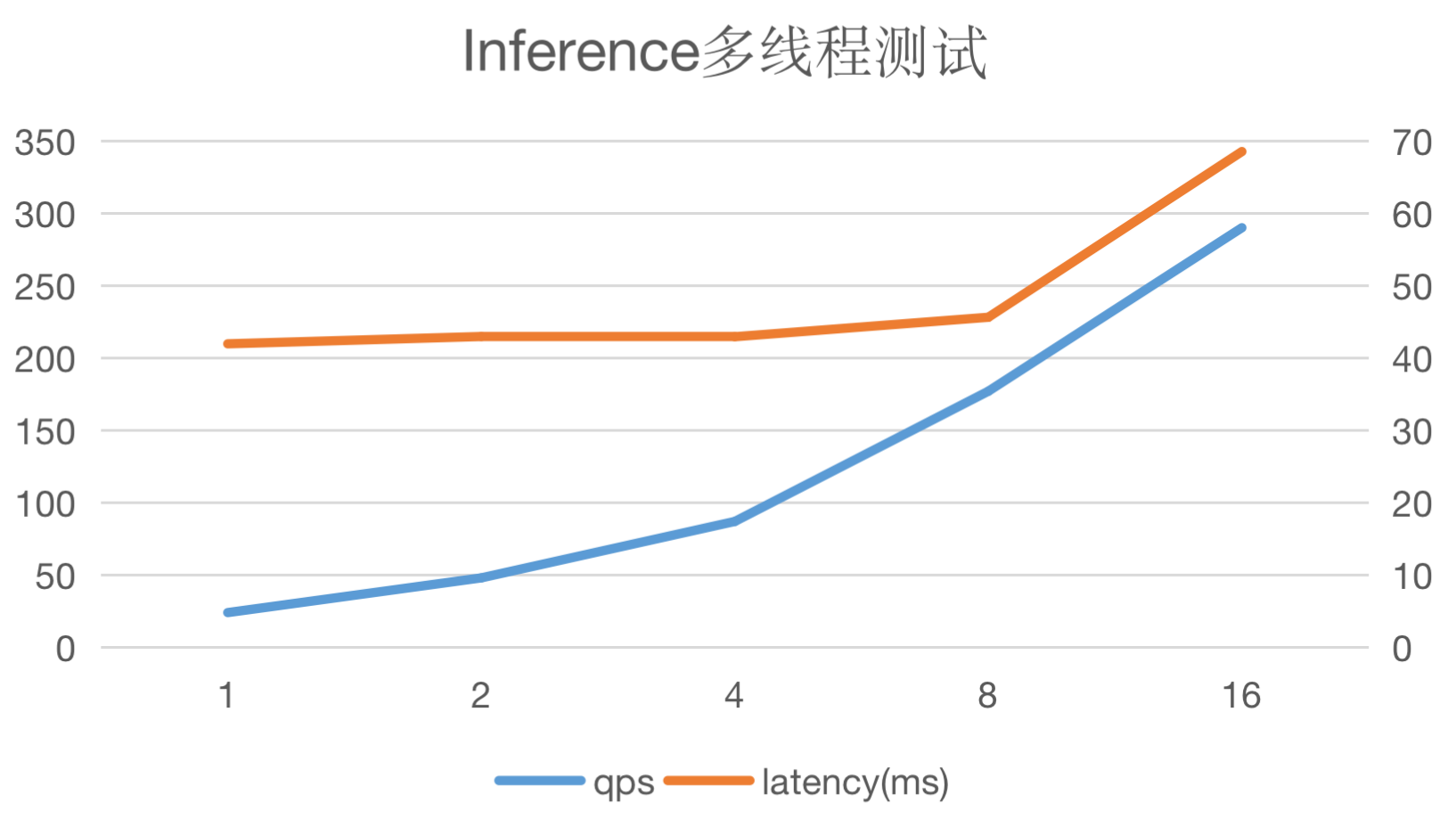 image
此处使用MobileNetV1进行测试,batch_size设定为1,线程数从1递增至16。可以看出QPS与线程数呈线性关系,同时请求latency变化不大。
image
此处使用MobileNetV1进行测试,batch_size设定为1,线程数从1递增至16。可以看出QPS与线程数呈线性关系,同时请求latency变化不大。